4.2-)Ejercicio de deriv, cruzadas
Transcripción
4.2-)Ejercicio de deriv, cruzadas
Ejercicio 4 Determine las funciones derivadas parciales de primer orden, de la siguiente función: fx para (x, y) 0 fx para (x, y) = 0 f (0,0) x f(h,0) = 0 f(0,0) = 0 lim h0 f (h,0) f (0,0) h f (0,0) x Luego: F(0,0) = 0 Función Derivada parcial de primer orden lim 0 0 0 h0 h fy para (x, y) 0 fy para (x, y) = 0 f (0,0) y f(0,h) = 0 f(0,0) = 0 lim h0 f (0, h) f (0,0) h f (0,0) y Luego: F(0,0) = 0 Función Derivada parcial de primer orden lim 0 0 0 h0 h Parte b) fxy para (x, y) = 0 fx (0,0) y lim h0 fx(0, h) fx(0,0) h fx (0,0) y fx(0,h) = -h fx(0,0) = 0 lim h 0 1 h0 h fxy = -1 Luego: fyx para (x, y) = 0 fy (0,0) x fy(h,0) = h fy(0,0) = 0 Luego: lim h0 fy(h,0) fy(0,0) h fy (0,0) x lim h 0 1 h0 h fyx = 1 Las derivadas cruzadas son diferentes en (0,0), luego no cumple el teorema de Schwarz




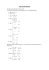



![0{ − IR 2 senh eex − = )( )( xtg xK = 0)(` ≥ xf ≥ )(` ],[ bax 0{ − IR 2 senh eex − = )( )( xtg xK = 0)(` ≥ xf ≥ )(` ],[ bax](http://s1.doczz.es/store/data/005144026_1-f30e6ebd7d5b6b5435a8e23bb88fd90c-70x70.png)